Gelan Air Fin Cooler is a perfect choice. It works well and keeps things cool all the time. It is strong, easy to use, and lasts a long time. Gelan is suitable for many cooling jobs because it works fast and needs little care. The Gelan cooler can cool both minor and significant places. It has a simple design, which makes it easy to use for everyone. It keeps heat away from the fluid, so it does not need much fixing. It also costs less to run, which saves money. Gelan is made to help you cool things easily and safely.
Gelan pipes are very safe. We use unique metal to make our pipes strong. The pipes need to be drained to stay good. Draining helps stop rust. Rust makes pipes weak.Our pipes are thin and robust. They help move heat fast. They use less energy. The pipes are light and easy to use. Many people like them. They use them to clean water and in factories. The fins stop wind and dust. The fins on the pipes are strong. This keeps the pipes clean. Even when it is tough, the pipes stay strong. This saves energy. Use our pipes. The heat stays inside. They are safe and robust. They last a long time. They are easy to use and not too costly. People all over the world use them.

An Air Fin Cooler (AFC) is a heat exchange device used to cool fluids or gases by utilizing air as the cooling medium. It’s commonly used in various industries, such as petrochemical, power generation, and HVAC, for cooling oil, gas, or other fluids. Here are the key specifications of an Air Fin Cooler:
These specifications can vary based on the application, operating conditions, and the specific needs of the installation. Proper design and material selection are crucial for maximizing the efficiency and lifespan of the Air Fin Cooler.
These features make the Air Fin Cooler a practical, efficient, and adaptable solution for industrial cooling applications across various sectors.
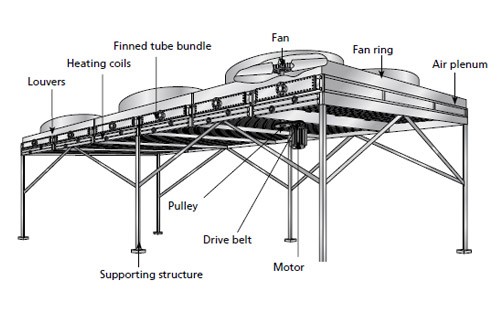
Air fin coolers, also known as air-cooled heat exchangers (ACHEs), are widely used across various industries for heat transfer and cooling purposes. They are particularly effective in situations where water is scarce, expensive, or unavailable for cooling, or where space constraints or environmental concerns require a more sustainable cooling solution. Here are some specific applications of air fin coolers:
Application: Air fin coolers are commonly used in power plants to cool the compressor exhaust, generator sets, and turbine exhaust gases. They are often used in place of traditional water cooling systems when water availability is limited or for cooling air from heat recovery systems.
Advantages: They reduce the need for large amounts of cooling water, which can be important in areas with water scarcity or environmental regulations.
Application: In oil refineries, petrochemical plants, and offshore platforms, air fin coolers are used to cool various fluids such as hydrocarbons, lubricating oils, and gas streams. They are especially beneficial in remote locations where access to cooling water is difficult.
Advantages: Air fin coolers are highly effective in these settings where space is limited and water availability is not guaranteed.
Application: Air fin coolers are used to cool process fluids in chemical plants, particularly in heat exchanger systems for products such as chemicals, solvents, and gases. These coolers help to maintain specific temperature ranges for chemical reactions and prevent overheating in reactors.
Advantages: Air-cooled heat exchangers are ideal for handling aggressive chemicals that may cause corrosion or scaling in water-cooled systems.
Application: In large HVAC systems, air fin coolers are used to cool refrigerants and air-conditioning systems, particularly in industrial and commercial applications. They help maintain optimal operating temperatures for chillers and condensers.
Advantages: They are used in areas where water-cooling towers might be impractical, such as in buildings with limited access to water supplies.
Application: On ships and offshore platforms, air fin coolers are used for cooling the engines and auxiliary equipment. In marine environments, cooling systems are crucial for maintaining efficient operation, especially where seawater may not be usable due to contamination or fouling.
Advantages: They are corrosion-resistant and effective in high-salinity environments, where traditional cooling systems would be less efficient.
Application: Air fin coolers are used in compressed air systems to cool the compressed air after it leaves the compressor before it is sent for storage or further use. They help in reducing moisture and maintaining the air quality for various industrial applications, including pneumatic tools and automation systems.
Advantages: They provide efficient cooling without the need for water and ensure the air remains dry and free from contaminants.
Application: In the petrochemical industry, air fin coolers are used in processes such as gas dehydration, liquefied natural gas (LNG) cooling, and crude oil cooling. They cool hot gases and liquids, which is essential for improving the safety, efficiency, and reliability of petrochemical plants.
Advantages: They provide a space-efficient solution for cooling fluids at high temperatures and can be customized to meet specific needs in these high-demand environments.
Application: Air fin coolers are used for cooling the air and water used in food processing and beverage manufacturing plants. In some cases, they are used for cooling the air in dry warehouses or areas where water cooling is not feasible.
Advantages: They can reduce the risk of water contamination in the production of food and beverages while still providing effective cooling.
Application: In data centers, where heat management is critical for the safe operation of servers, air fin coolers are used as part of the overall HVAC system to cool the server rooms and control room environments.
Advantages: They help maintain energy-efficient cooling without requiring extensive water-based cooling systems, making them ideal for locations with limited access to water.
Application: Air fin coolers are used in cooling systems for mining equipment (e.g., crushers, grinders) and in processing plants for mineral extraction processes, where heavy equipment generates significant heat.
Advantages: They provide a robust and low-maintenance cooling solution in harsh environments, such as mines, where water is not easily accessible.
Application: Air fin coolers are often used in waste heat recovery systems to cool the hot exhaust gases or fluids from industrial
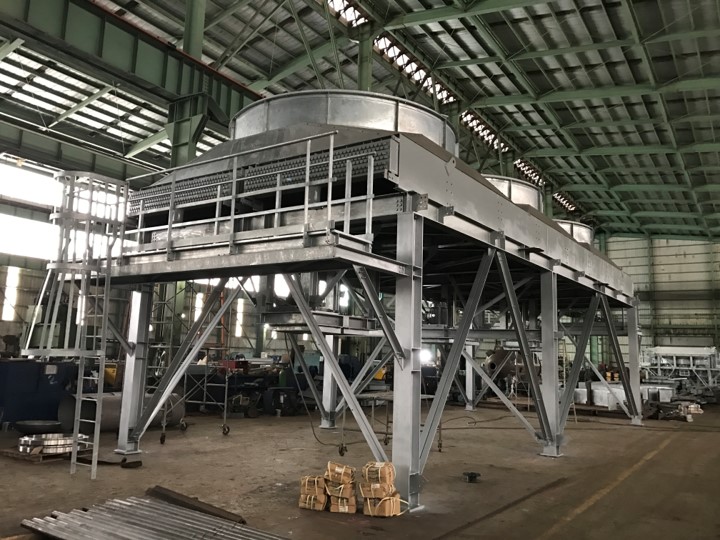
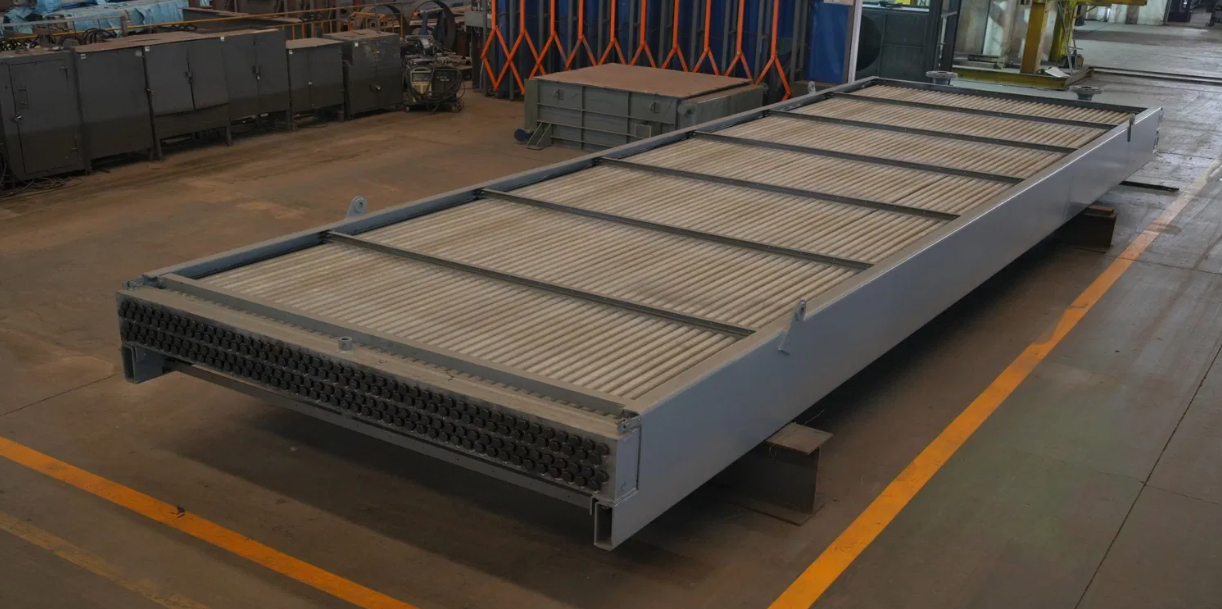
It has a simple and intelligent design. It uses cooling fins to make fluids cool. The fluid moves through tubes, and these tubes have cooling fins around them. The cooling fins help the air take the heat away from the fluid. A fan called a fin fan cooler blows air over the fins. This makes the heat go away faster, which keeps the fluid cool. The cooler is easy to keep clean, which helps it last a long time and keeps things safe. The fan is significant because it allows the cooling to go faster. When the fan blows air over the fins, the heat goes away quickly. The simple design also means fewer parts that can break, which makes it easy to use for a long time without much trouble. The cooler is built to help many different places stay cool.


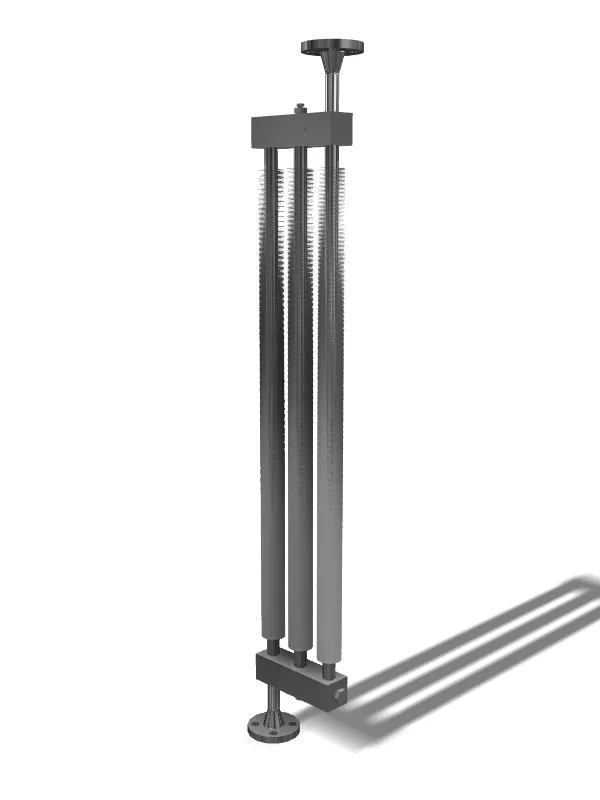
In extrusion, the fins come from the tube itself. The metal of the tube is pushed out to make fins. The fins and the tube are one piece. This makes the fins very strong. They do not come off. Extruded fins last a long time. They stay on well.
In the embedded way, the tube is cut to make slots. The fins are put in these slots. This makes the fins fit tightly. The fins touch the tube, so they move heat well. The fins stay in place, even when it gets very hot. This helps the tube work well for a long time.
In welding, the fins are joined to the tube with heat. This makes the fins stick very well. The fins do not fall off. Welded fins stay in place, even when it is very hot. Power plants use welded fins because they are strong. Welded fins help move heat and make the tubes work well. They do not break easily and stay on very well.
In a forced cooler, fans are placed under the cooling fins. These fans push air up through the fins to cool the fluid inside the tubes. This type of cooler works well when the weather is not too hot. It is also easy to clean because the fans are at the bottom, and you can reach them easily. The forced draft cooler is suitable for many jobs that need steady cooling but not extreme cold.

In an induced draft air cooler, fans are above the cooling fins. The fans pull air through the fins. This helps cool the fluid, even in hot places. It keeps the temperature steady and stops the hot air from coming back in. This makes it very good for hot places where keeping things cool is very important. Induced draft coolers are used when the cooling must be strong and even all the time.
This one has no fans. It uses natural air to move over the cooling fins. This type of cooler is used where there is little power or where people want to save energy. It is slower than the others, but it is quiet and needs less care. It is suitable for places that do not require quick cooling but need something that works without much power.
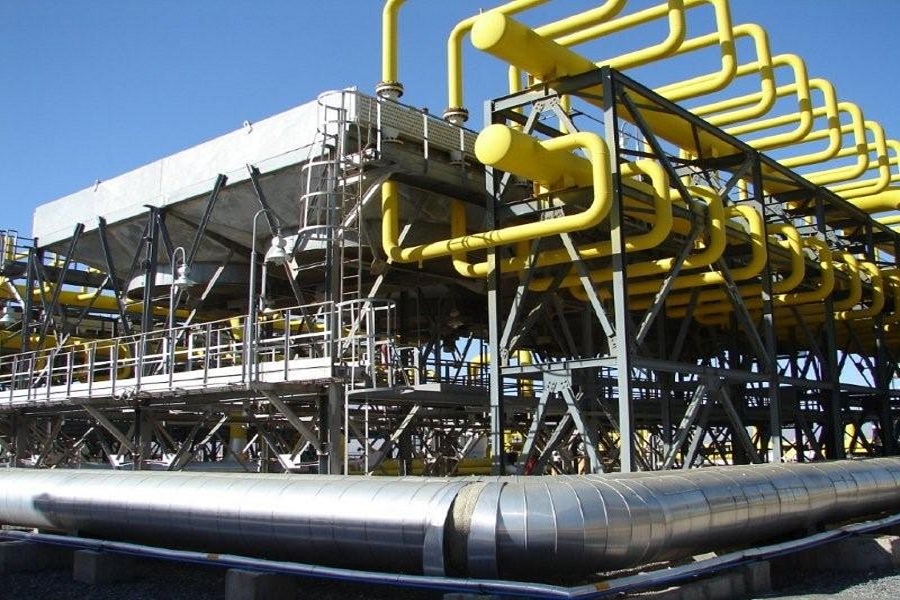




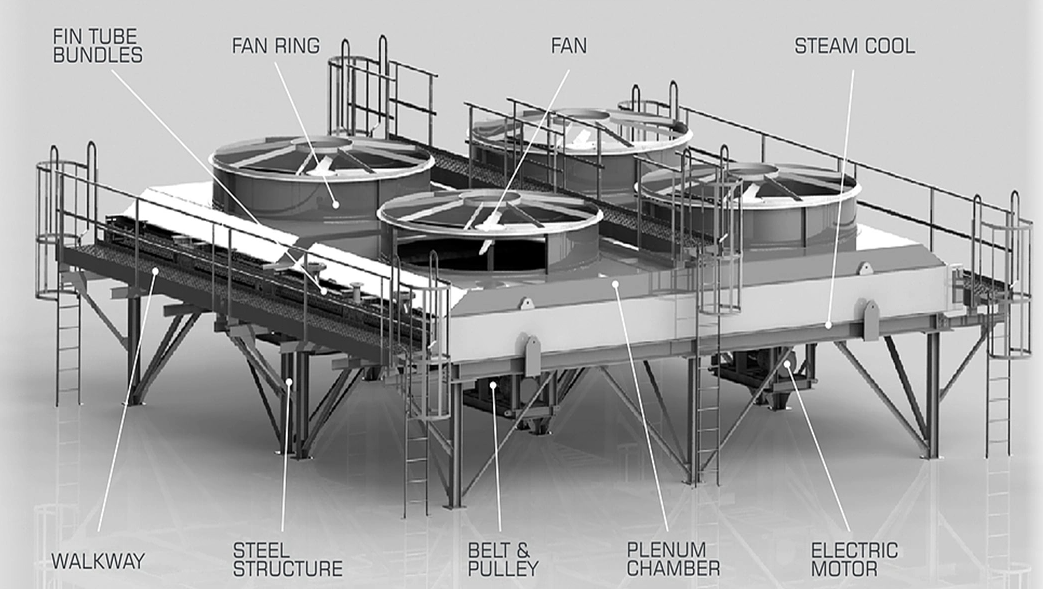
These are used in many places. They are used in oil plants, chemical plants, power stations, and other areas that need cooling. They help keep things at the right temperature so machines do not get too hot and break down. Oil plants keep oil cool. In chemical plants, they keep things at the right temperature for making products. Power stations cool fluids that help make power. These coolers are helpful because they work well in many different places. They help keep machines working and keep everything safe.
It is a machine that cools fluids. It uses fans and cooling fins to take heat away from fluids. It helps keep things cool and safe.
Cooling fins help heat move from the fluid to the air. This makes cooling faster and better. The fins give more space for the heat to move away.
There are three main types: forced draft, induced draft, and natural draft. Each one cools differently and is suitable for different jobs.
A fin fan cooler helps take away heat fast. It is suitable for places like factories and power plants where strong cooling is needed.
Try to use a cooling fin comb to clean the fins. This helps keep the cooler working well and makes sure the air moves through the fins to cool the fluid.
Our Professional Project Manager will help you step by step. Welcome to compare price and Service
We do not share your personal information with third parties. By clicking the button, you consent to the processing of personal data.
Feel free to get in touch with us!

We are pleased to receive your letter and help you achieve your business goals. Fill in the form below to send us information or talk directly to our product experts by phone.
We will contact you within 1 hours, please pay attention to the email with the suffix “@gelanpetro.com”.